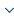1. Introduction
With the acceleration of urbanization in China, the protection and utilization of industrial heritage have become a hot spot of social concern. As a carrier of history and culture in a certain region, transforming connotation of industrial heritage into creative products and integrating with creative tourism can not only promote the protection process of industrial heritage, but also provide good support for the development and transformation of the local economy [1-2].
2. Conceptual Interpretation
Creative tourism refers to a form of tourism in which tourists participate in the culture and skills of the tourist destination, inspire their creativity, further stimulate their creative potential, and ultimately form a profound experience of the culture of tourist destinations. It has the characteristics of individuation, sustainability, and creativity [3]. Creative tourism resources exist objectively in a certain region. They attract tourists because of their novelty, peculiarity, and participation. While satisfying the enjoyment of novelty, entertainment, and experience, they can also be utilized by tourism and produce various tangible or intangible resources with economic, social, and environmental benefits [4].
Industrial heritage is a special historical memory and landscape of a city, which determines that it has great potential to become a creative tourism resource [5]. Industrial heritage tourism and creative tourism have strong consistency in content and characteristics. It is a new type of tourism based on traditional tourism, with industrial heritage as the core, which meets the needs of tourists by displaying factories, machinery and equipment, processes, and other activities. It focuses more on communicating with tourists and the experience process.
Changchun is one of the old industrial bases in Northeast China with a large industrial heritage. It is the trend of future development to make effective use of industrial heritage as creative tourism resources, integrate them with creative tourism, highlight the regional and humanistic connotations, and satisfy the protection and development objectives of its own while producing multiple benefits.
3. Survey of the Status of Changchun Industrial Heritage as Creative Tourism Resources
3.1. Industrial Development of Changchun
Changchun’s modern industrial development can be divided into three stages according to its formation time.
(1) Industrial start-up period (1898-1931). With the construction of the Middle East Railway and the Nanman Railway, Changchun had become a prosperous agricultural by-product transportation and marketing center in the middle of Northeast China. However, due to the backward technology, the industrial development was mainly dominated by handicrafts and small family workshops. Shops, granaries, and handicraft workshops have emerged. It is represented by the grain processing industry (such as the Kangde Fire Mill, Yuchangyuan Flour Mill, Fushun Hou Flour Mill, etc.), the coal mining industry, and electric power production (Figure 1) [6-7].
Figure 1.
Figure 1.
The main industrial heritages of Changchun industrial start-up period
(2) Industrial malformed development period (1932-1947). After Japan launched the war of aggression against China, Changchun was defined as a “consumer” city, with almost no substantial heavy industrial enterprises. In the light industry, by 1940, the assets of six large-scale Japanese enterprises, such as the Manchuria Ceramic Warlock Association, Puppet Manchuria Imperial Printing Factory, and Xinjing Paper Mill, accounted for over 90% of the Changchun light industry. After the recovery of Changchun in 1945, most enterprises closed down or stopped production, and the number of light industrial enterprises decreased from 64 in 1941 to 9 (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Figure 2.
The main industrial heritages of Changchun industrial malformed development period
(3) Industrial recovery and improvement period (1948-1965). In 1953, after three years of economic adjustment, under the unified deployment of the National Planning Group, the document of Changchun Master Plan was issued. At the same time, the first Five-Year Plan for the development of the national economy was implemented, and large-scale economic construction began. While accelerating the development of light industry, breakthrough progress had been made in heavy industry, which had formed a heavy industry structure mainly consisting of automobile production, tractor manufacturing, and transportation machinery manufacturing (such as the Changchun First Automobile Factory, Changchun Tractor Factory, Changchun Bus Factory, etc.). The bicycle industry, clock industry, and other light industry sectors had also been developed. Finally, the transformation from a “consumption-oriented city” to a comprehensive industrial city was achieved (Figure 3) [8].
Figure 3.
Figure 3.
The main industrial heritages of Changchun industrial recovery and improvement period
3.2. Types of Changchun industrial Heritage as Creative Tourism Resources
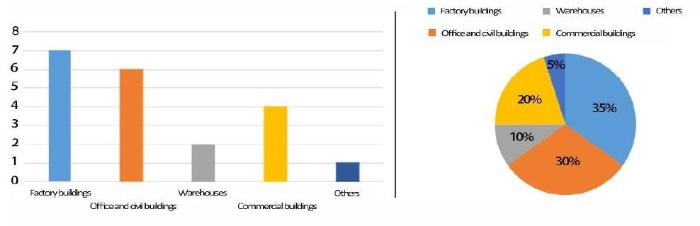
Based on the List of Key Industrial Heritage Protection in Jilin Province, the author has investigated 31 major industrial heritages in Changchun. It includes three categories and ten items of the food industry, machinery, and so on. Overall, the status quo is not optimistic (Figure 4). According to the use and preservation status of the plant, it can be divided into three categories:
Figure 4.
Figure 4.
Statistics of Changchun industrial heritage protection units
(1) Enterprises are shut down and factories are idle, abandoned, or used as auxiliary functional buildings (temporary warehouses). This type of industrial heritage, such as the Kant Fire Mill (Figure 5) and Changchun Tractor Plant (Figure 6), accounts for about 50% of the total survey. After some industrial heritages are identified as “cultural relics protection units”, there is no further consideration of measures for protection and utilization. The environmental pollution in the plant area is severe, and the building is in disrepair. This type of industrial heritage cannot be included in the creative tourism system in the short term.
Figure 5.
Figure 5.
The broken Kant fire mill factory
Figure 6.
Figure 6.
The idle Changchun tractor factory
(2) Enterprises stop production and replace the function. This type of industrial heritage, such as the Changchun Fur Factory (Figure 7) and Changchun Brewing Factory 2 (Figure 8), accounts for about 20% of the total. Some industrial heritage sites are converted into residential areas (Figure 9), shopping centers (Figure 10), and so on. The function and appearance of these buildings have been changed significantly and only some industrial elements were retained, which has no significant features and is of little value in the development of tourism.
Figure 7.
Figure 7.
Changchun Fur Factory
Figure 8.
Figure 8.
Changchun Brewing Factory 2
Figure 9.
Figure 9.
Vanke Blue Mountain
Figure 10.
Figure 10.
Eurasia Marketplace
(3) Enterprises are still in production and continue to operate. This type of industrial heritage, such as the Changchun First Automobile Factory (Figure 11) and Changchun Bus Factory (Figure 12), accounts for about 30% of the total. Most of these factories are national key enterprises built during the First and Second Five-Year Plan period, relying on national support, follow-up personnel training, advanced technology and equipment, etc [9]. These factories maintain their original production, and the environment and building status are well preserved, which can well represent the history of local industrial culture. These can be fully utilized as creative tourism resources in industrial heritage tourism.
Figure 11.
Figure 11.
Photos of Changchun First Automobile Factory
Figure 12.
Figure 12.
Photos of Changchun Tractor Factory
4. Feasibility Analysis of Changchun Industrial Heritage as Creative Tourism Resources
4.1. Characteristics of Changchun Industrial Heritage as Creative Tourism Resources
Changchun industrial heritage has three distinctive characteristics as creative tourism resources:
(1) Abundant architectural type (Figure 13). Workshops, offices, and warehouses account for 70% of the total. These three types of buildings have spacious and changeable interior space, large building volume, strong plasticity in the transformation [10], and can also save costs for investment in the early stage of creative tourism development.
Figure 13.
Figure 13.
Statistics on the main types and proportions of Changchun industrial heritage
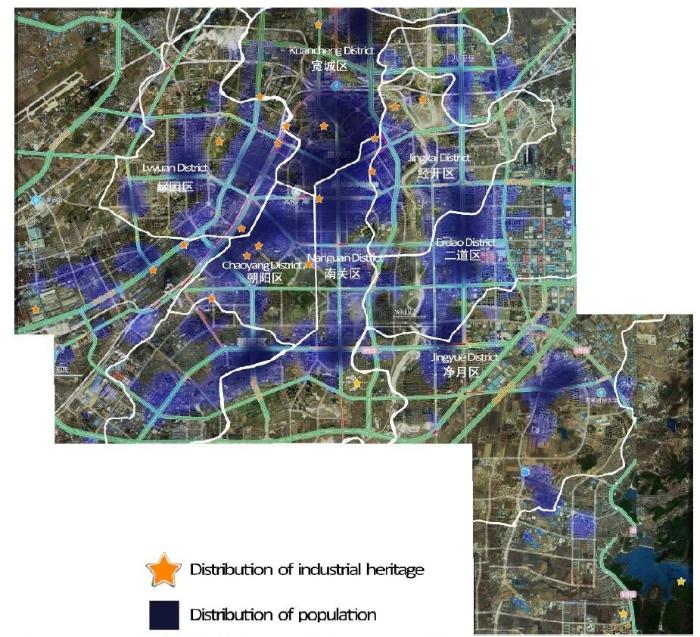
(2) Concentrated distribution. Industrial heritages mainly concentrate in the Kuancheng, Chaoyang, and Lvyuan districts in Changchun (Figure 14), which brings convenience to tourism development and management, shortens tourist routes, and reduces travel time. According to the thermal distribution map of the population, it can be seen that the population around the industrial heritage is densely distributed, and the three districts are old urban areas. The industrial atmosphere is good, and social recognition is high. People are more willing to participate in it, which lays a good foundation for creative tourism on the theme of industrial heritage.
Figure 14.
Figure 14.
Comprehensive distribution map of Changchun population and major industrial heritage
(3) The distinctive brand of “red” era. There were nine industrial heritages built in Changchun during the First Five-Year Plan and the Second Five-Year Plan. They not only occupy an important position in the history of Changchun industry, but also witness the industrial development of New China. They have been deeply imprinted by the times.
4.2. SWOT Analysis of Changchu’s Industrial Heritage as Creative Tourism Resources
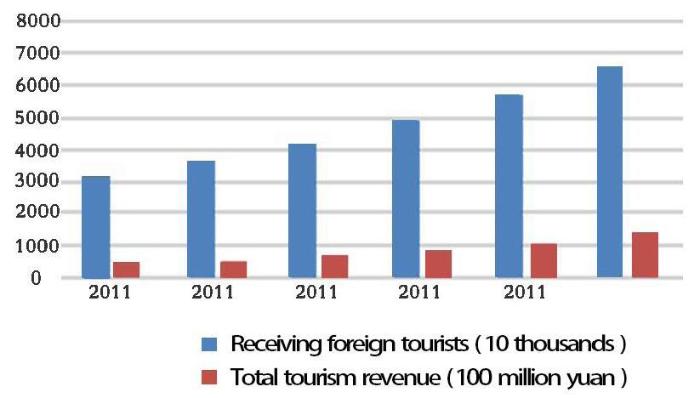
(1) Strengths. Changchun is an important transit station in Jilin Province and even in Northeast China because of its superior geographical position, and it has a unique urban culture. There is a large number of industrial heritages in Changchun and surrounding areas, which can be linked to Changchun to play an “aggregation effect”, complement each other, and develop synergistically (Table 1). In addition, the potential of Changchun’s tourist market is huge, with an average growth rate of 21% in the past five years (Figure 15), which depicts a bright future for Changchun's industrial heritage tourism.
Table 1. Number of industrial heritages in other cities and counties in Jilin Province
| Area | Jilin | Yanbian | Tonghua | Songyuan | Jiutai | Dehui | Huadian | Siping | Baishan | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Existing total | 75 | 17 | 17 | 9 | 23 | 8 | 11 | 34 | 11 | 226 |
Figure 15.
Figure 15.
2011-2016 Changchun tourism reception and tourism income statistics
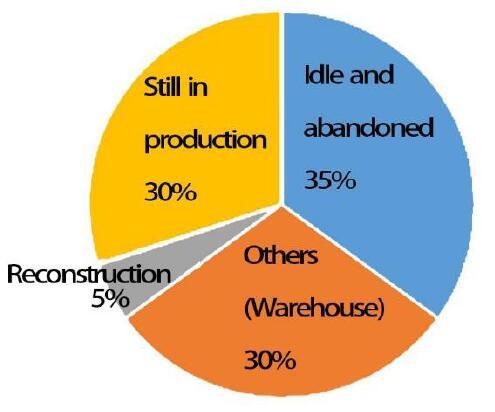
(2) Weaknesses. The long and cold winter in Changchun has a great impact on heritage tourism. Industrial heritage tourism infrastructure is weak, and 35% of the existing industrial heritage has been idle for a long time (Figure 16). The problem of industrial pollution remains to be solved. Public transport, guide signs, and other tourism service systems need to be strengthened. There are few enterprises that can make full use of these industrial heritage tourism resources.
Figure 16.
Figure 16.
Current status of Changchun industrial heritage
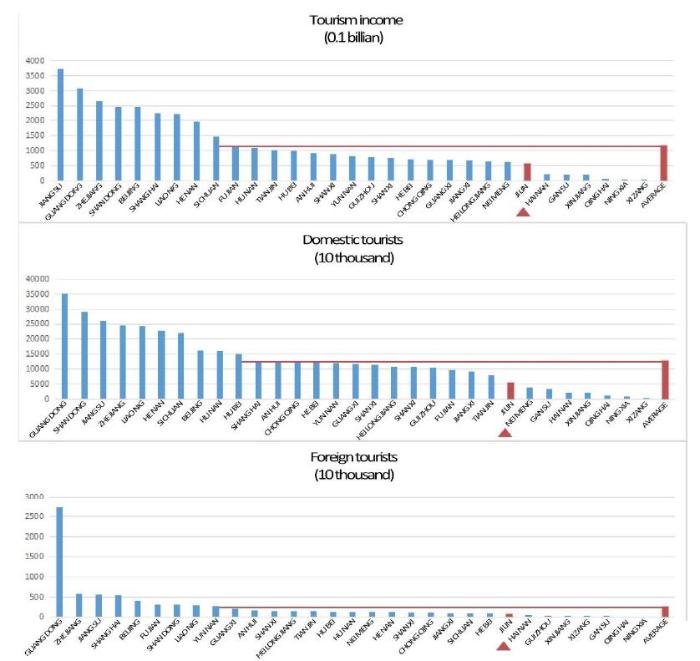
(3) Opportunities. In 2016, although the tourism industry in Jilin Province maintained a good momentum of sustained and rapid development, it did not reach the domestic average level in terms of tourism income, domestic tourists, and the number of inbound tourists. There is a great room for development (Figure 17). In 2017, Changchun was on the list of national historical and cultural cities, which will undoubtedly greatly promote the development of industrial heritage tourism.
Figure 17.
Figure 17.
2016 Jilin Province tourism statistics
(4) Threats. Changchun industrial heritage tourism has a cooperative and competitive relationship with the surrounding cities, especially with the same type of industrial cities. How to make a thorough study on the differential development, creatively combine regional tourism resources, and form competitiveness is an issue that needs to be discussed in depth.
5. Integrated Development Strategy, Mode, and Overall Planning of Changchun’s Industrial Heritage as Creative Tourism Resources
5.1. Integrated Development Strategy
Regarding the protection of industrial heritage as a “high-voltage line” for tourism, all development activities can only be implemented on the basis of reasonable and effective protection [11]. The Changchun Municipal Government is in charge of the overall development of industrial heritage tourism, giving full play to creativity, focusing on the differentiation of tourism products, and improving service quality through technology. Combine industrial heritage tourism with modern industrial experience to enhance the sense of participation of tourists, and at the same time carry out targeted design in accommodation, transportation, souvenir sales, and other aspects. Develop long-term and dynamic plans for industrial heritage tourism development. Improve supporting infrastructure.
5.2. Integrated Development Mode
In combination with the different types of creative tourism resources, the development of creative tourism resources of industrial heritage in Changchun can mainly adopt the following modes: science and technology + museum mode, experience + shopping mall mode, leisure + community mode, and fashion + literary creation mode.
Take Dingfengzhen Food Factory as an example, and transform it into a food experience mall. The video is used to describe the vicissitudes of the past hundred years, understand the food production process, and participate in the making of food. To mobilize the enthusiasm of tourists, the whole process emphasizes experiential. Through a series of services, visitors can experience the pleasure of industrial heritage tourism and finally recognize the value of industrial heritage tourism.
5.3. Overall Planning Intention of Changchun Industrial Heritage Creative Tourism
In accordance with relevant national laws and regulations, such as “Jilin Province Tourism Development Master Plan”, national standards “Tourism Planning General Principles”, and National Tourism Administration “Tourism Planning Management Measures”, and combined with the types and methods of creative tourism resource development, this paper proposed the overall planning intention of Changchun’s industrial heritage creative tourism.
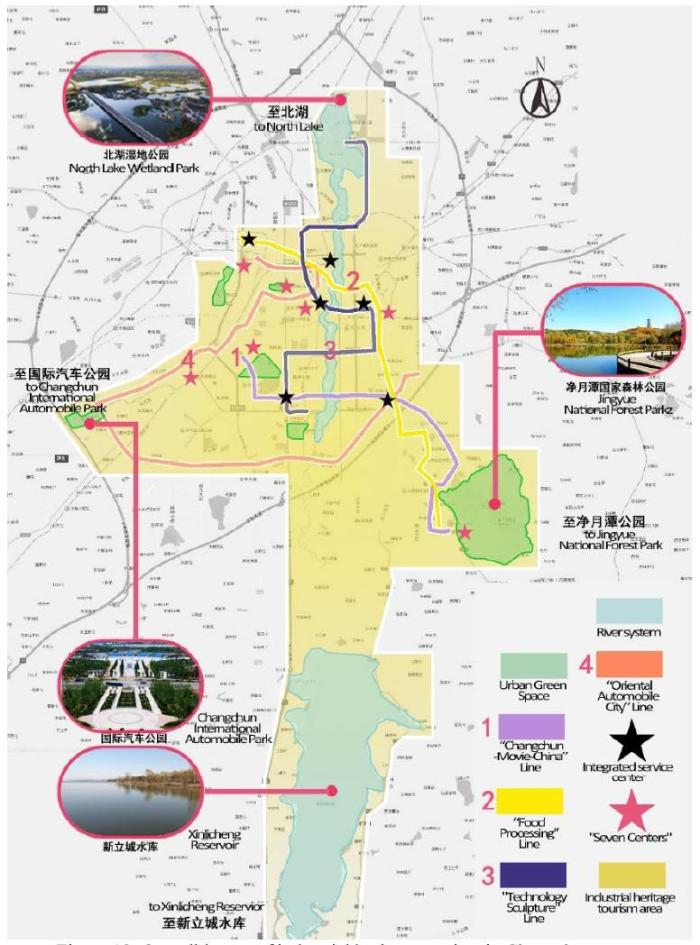
(1) The overall layout of creative tourism of Changchun industrial heritage is “One District”, “Four Lines”, and “Seven Centers” (Figure 18).
Figure 18.
Figure 18.
Overall layout of industrial heritage tourism in Changchun
“One District” is “Industrial Heritage Tourism Area”, from Beihu Wetland Park in the north, Xinlicheng Reservoir in the south, International Automobile Park in the west, and Jingyue Forest Park in the east, spanning 31.7km from north to South and 22.5km from east to west. It includes Changchun’s main industrial heritage and other tourist resources in the city.
“Four Lines” are based on Changchun's characteristic industries, forming four industrial heritage tourist lines: “Changchun-Movie-China”, “Food Processing”, “Technology-Sculpture”, and “Oriental Automobile City”. At the same time, the industrial heritage of Changchun will be combined with the existing mature scenic spots and tourism projects to form a linkage effect. Make full use of geographical advantages to promote the development of new industrial heritage tourism projects.
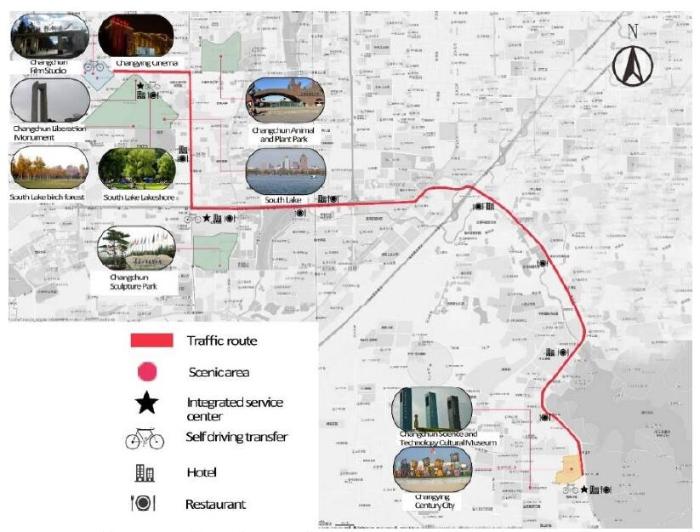
“Changchun-Movie-China” is a movie-themed tour line. Changchun Film Studio and Changying Century City are the main industrial heritage landscapes, and Nanhu Park, Animal and Plant Park, etc. are auxiliary attractions (Figure 19). Changying was the first film studio in China and is irreplaceable in the history of Chinese cinema. The old factory covers an area of 37,549 square meters, including the main building, six studios, and the mixed studio. With the theme transformation, the videos, pictures, and historical objects can be used to objectively reflect the history of the development of Changying. Changying Century City is a movie theme park, bringing together the most advanced movie technology in the world today. Strengthen the sense of participation of tourists from various aspects, brought by contemporary film technology from the visual and auditory perspectives.
Figure 19.
Figure 19.
“Changchun-Movie-China” industrial heritage tourism line
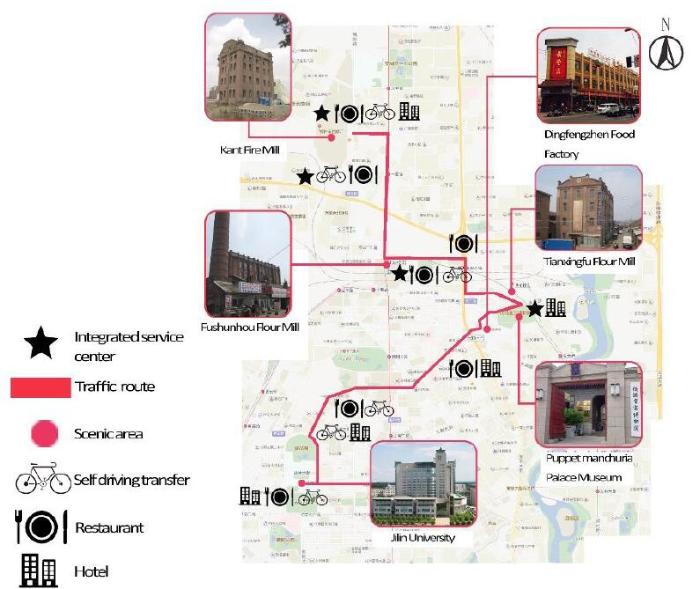
“Food Processing” is an industrial heritage tourism line with the core of the Kant Fire Mill Museum (after renovation), Tianxingfu Flour Mill and Fushunhou Flour Mill (after renovation) and Dingfengzhen Shopping Plaza, which is 30 kilometers long (Figure 20). In the history of Changchun, the first four-story red brick building, first elevator, and first large-scale complete sets of machinery and equipment were born in Kant Fire Mill. It can be transformed into a Kant Museum with the theme of “Education and Experience”. Historical materials and photographs can be provided for tourists to visit and reproduce the traditional production techniques of that year. Relying on its superior geographical position, Tianxingfu Flour Mill and Fushunhou Flour Mill will be transformed into a “gourmet city”, gathering the special snacks and gourmet foods around Changchun, so that visitors can come here and taste the delicious food of Jilin Province and even the whole northeast. Dingfengzhen is a famous food enterprise in Changchun. It was established in 1919. By visiting the food production workshop, tourists can understand the process and technology of traditional food production in Northeast China, taste and produce local characteristic food in person, and feel the charm of industrial heritage from the perspective of vision and taste. At the same time, the corresponding express delivery service can be used to deliver the food purchased by the tourists and produced by themselves.
Figure 20.
Figure 20.
“Food Processing” industrial heritage tourism line
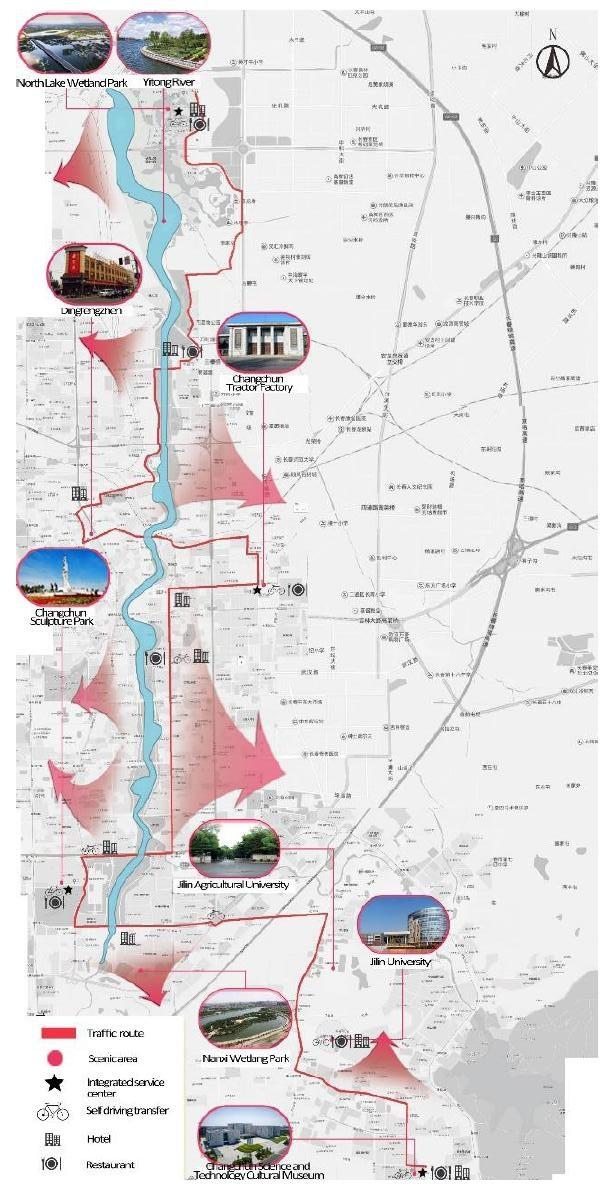
“Technology-Sculpture” is an industrial heritage tourism line with the core of Changchun Tractor Factory, Changchun Science and Technology Cultural Museum, and Sculpture Park, and it is 37.6 kilometers long (Figure 21). The entire tourist route runs through Changchun’s “Mother River”, Yitong River. While visiting the industrial heritage, tourists enjoy the beautiful scenery along the bank, which also implies the past and present of Changchun. The industrial buildings in Changchun Tractor Factory are mostly high-span factory buildings, with spacious and bright interior space, which is convenient for later transformation. It can be transformed into multi-functional spaces, such as galleries, exhibition halls, cafes, and restaurants. Changchun Sculpture Park is located at the southern end of People’s Avenue. It is the first batch of national key parks, national 5A tourist attractions, and also a theme park integrating world sculptures. The Changchun Science and Technology and Culture Museum is a collection of the China Optical Science and Technology Museum, Jilin Province Museum, and Technology Museum. Through scientific, intellectual, and interesting exhibitions and interactive forms, the three pavilions present the history, culture, science, and technology of Changchun to visitors in a well-rounded way.
Figure 21.
Figure 21.
“Technology-Sculpture” industrial heritage tourism line
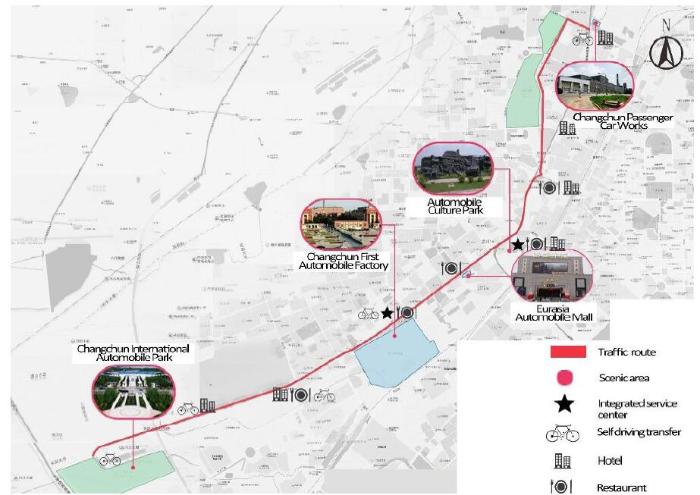
“Oriental Automobile City” is the industrial heritage theme tourism line centered on automobile manufacturing. Changchun First Automobile Factory, Automobile Culture Park, and Changchun International Automobile Park are the main scenic spots with a total length of 16.6 km (Figure 22). Changchun First Automobile Factory was one of the key projects built during the First Five-Year Plan period in China. The first Jiefang truck in New China came from here. Tourists can not only walk into the production workshop and visit the modern production line, but also understand the history of automobile development in China. Tourists can even participate in some automobile assembly work themselves. They can also design the style and color of automobiles according to their preferences and give their suggestions for automobile design. The automobile culture park has six functional areas. Changchun International Automobile Park is the largest car theme park in the country. Tourists enjoy the collision between cars and artistic creation.
Figure 22.
Figure 22.
“Oriental Automobile City” industrial heritage tourism line
“Seven Centers” are based on the seven units of Changchun First Automobile Factory, Changchun Tractor Factory, Dingfengzhen Food Factory, Changchun Film Studio, Changying Century City, Changchun Locomotive Factory, and Changchun Bus Factory, which operate well or have little difficulty in rebuilding, and they can be well protected and developed.
(2) The stages and objectives of Changchun's industrial heritage tourism planning
Initial goal planning can be five years (2019-2023). In the initial stage, we should establish the “creative tourism brand of industrial heritage” to solve the quality problems of industrial heritage buildings, protect or transform them reasonably, and repair or improve the scenic environment and the supporting facilities, so as to achieve the strict standards of scenic business.
The medium-term planning can be ten years (2024-2033). In the first five years, the industrial heritage tourism “line” will be formed; in the second five years, existing tourism resources will be fully utilized to integrate with the tourism “line”, and Changchun’s characteristic festivals, exhibitions, and industrial heritage tourism lines will be combined, such as film festivals, ice and snow festivals, Agricultural Exposition, Automobile Exposition, Sculpture Exhibition, etc. Actively develop the surrounding cities and counties of Changchun (such as Yanbian, Jilin, Siping, Songyuan, etc.) and the “line” of industrial heritage tourism in Changchun to form creative tourism "zones" of industrial heritage and expand the impact.
The long-term target plan can be five years (2034-2038). With Harbin, Changchun, Shenyang, and Dalian as the main axis, the joint development of creative tourism of industrial heritage will be carried out, and the tourism resources of the other two provinces will be integrated to form tourism projects with industrial heritage as the theme.
6. Conclusions
Creative tourism is the main trend of tourism development in the era of globalization and also a powerful driving force to promote the economic development of a city. In the specific operation process, there are five aspects of integration: the integration of industrial heritage property rights, investors, and operators; the integration of economy, society, land, environmental protection, culture, and other aspects in the planning process; the integration of various financing modes in the development process; the integration of related industries in the process of industrial replacement; and the integration of talents in various aspects in the whole process.
Integrating the industrial heritage of Changchun City with creative tourism, exploring regional factors in the city, and utilizing the existing industrial heritage resources based on protection and rational development will play a vital role in promoting the development of regional tourism, enhancing economic strength, and promoting the coordinated development of society.
Acknowledgments
This paper is the project subsidized by soft science research of the Department of Science and Technology of Jilin Province (No. 20160418023FG).
Reference
“The Integration of Creative Tourism and Theme Tourism: Motivation and Realization Path,”
“ Life and Death of Architecture: Research on the Reuse of Historic Buildings,”
“Creative Turn and Creative Tourism,”
“Classification, Evaluation and Spatial Variation of Urban Creative Tourism Resource,”
“Four Major Paths for the Development of Cultural and Creative Industries and Related Industries,”
“The Modern and Contemporary Historical Records of Changchun, ”
“Changchun Modern Architecture, ”
“History of Modern Architecture in China, ”
“History of Changchun Passenger Car Works ( 1954 -1951), ”
“Research on Protection and Recycling of Industrial Building Heritage of Xi’an, ”
“Introduction of Historical City Protection - An Integrity Method of Cultural Heritage and Historical Environmental Protection, ”